Planting Zones Explained: What They Are, Why They Matter, and How to Use Them in Your Garden

If you’ve ever brought home a beautiful plant only to watch it wither and die within weeks, the problem might not be your watering habits – it could be your planting zone.
Understanding your USDA Plant Hardiness Zone is one of the most essential steps toward creating a successful, resilient garden. Whether you’re growing vegetables, herbs, annuals, or perennials, knowing what zone you live in – and what that means for your plants – can make or break your garden’s health and productivity.
In this beginner-friendly guide, we’ll explain what planting zones are, how to find yours, and how to use that knowledge to plan a garden that thrives season after season.
What Are Planting Zones?
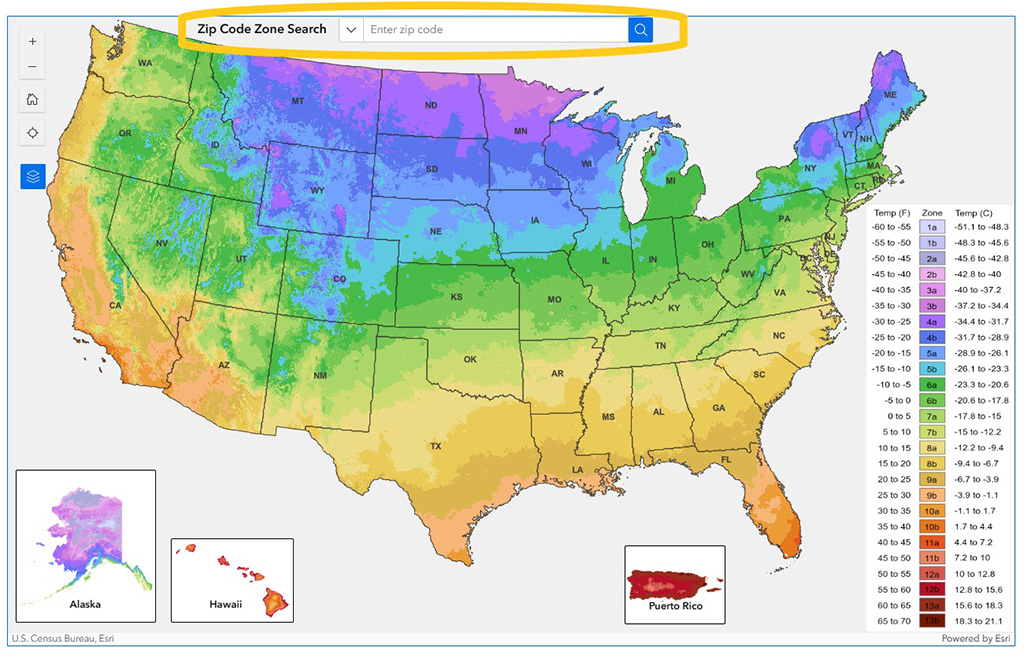
Planting zones, also known as USDA Hardiness Zones, were developed by the United States Department of Agriculture to help gardeners understand which plants are most likely to thrive in a specific location.
Each zone is based on the average annual minimum temperature for that area. Zones are divided into thirteen major regions (Zone 1 to Zone 13), and each of those is subdivided into subzones labeled “a” or “b.” The lower the number, the colder the average temperature in winter.
You can check your exact planting zone by entering your ZIP code on the official USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map.
Why Planting Zones Are Important for Gardeners
If you want your garden to flourish, planting the right plants at the right time in the right zone is key.
Here’s why planting zones matter:
1. Choose the Right Plants
Hardiness ratings on seed packets and plant tags tell you the lowest temperature a plant can survive. A perennial rated for Zones 5-9 likely won’t survive a Zone 4 winter. Using your zone to guide your plant selections helps ensure better survival and long-term growth.
2. Improve Plant Longevity
Understanding your zone helps you plan what will come back year after year (perennials) versus what needs to be replanted (annuals).
3. Time Your Planting Perfectly
Each zone has a unique growing season. Gardeners in Zone 4, for instance, may need to start seeds indoors in March, while Zone 9 gardeners can grow almost year-round. This helps avoid frost damage and poor yields.
4. Save Money and Time
When you plant zone-appropriate plants, you avoid the cost (and disappointment) of rplacing dead plants each season.
How to Find Your USDA Hardiness Zone
To determine your zone, use the interactive USDA map (see link above). Many plant nurseries, seed suppliers, and garden centers like Burpee, American Meadows, and Home Depot let you shop by zone.
What Planting Zones Don’t Tell You
Zones help you with cold tolerance, but they don’t cover everything. Consider these additional factors:
1. Summer Heat & Humidity
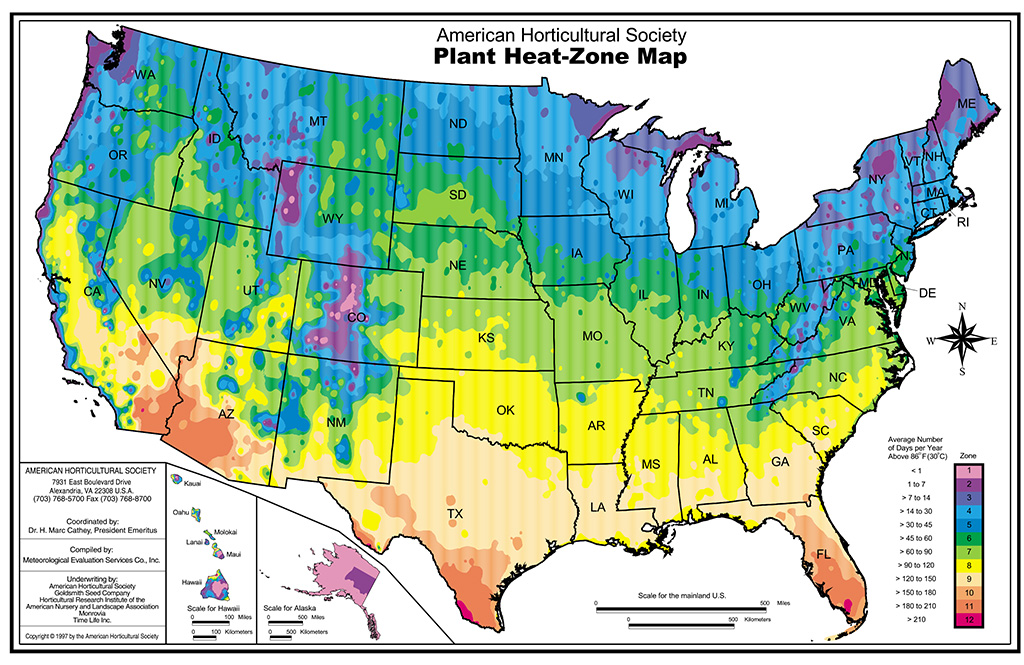
A plant may survive winter but struggle in extreme summer heat. Use the AHS Heat Zone Map by the American Horticultural Society to learn more about your local high temperatures.
2. Soil Quality & Drainage
Does your soil have a high clay content? Does it stay relatively moist or dry out immediately after a rain shower. Soil composition determines how well moisture is retained, and adequate drainage ensures that the plants do not become oversaturated with standing water.
3. Microclimates
South-facing walls, patios, and raised beds may stay warmer and allow zone-stretching.
4. Wind Exposure & Sun Hours
Shelter and sunlight can dramatically influence your plant’s health. Plants which are constantly beaten by the wind have little chance to thrive, and an overabundance of sunlight can be too much for some plants.
Recommended Plants by Zone
Choosing plants suited to your zone not only improves success, it creates the opportunity to enjoy low-maintenance, gorgeous results.
Best Plants for Zones 5-6:
- Lavender
- Coneflower
- Hostas
- Peonies (our favorite!)
Best Plants for Zones 7-8:
- Hydrangeas
- Coral Bells
- Black-Eyed Susan
- Salvia
Best Plants for Zones 9-11:
- Bougainvillea
- Hibiscus
- Citrus Trees
- Bird of Paradise
Final Thoughts
Planting zones are a secret weapon for home gardeners at every level of proficiency. By choosing plants that thrive in your region, you’ll save money, reduce frustration, and watch your garden flourish.
Whether you’re designing a pollinator garden, starting a vegetable patch, or filling containers on your patio, understanding your USDA zone is your first step to success.
